PHP Attributes, introduced in PHP 8.0, are a game-changer for writing cleaner, more expressive code. Let me break down what they are, why they matter, and how frameworks like Laravel use them.
What Are PHP Attributes?
Think of attributes as sticky notes you attach to your code. These sticky notes contain extra information (metadata) about your classes, methods, or properties that you can read later when your program runs.
Before PHP 8.0, developers used docblock comments for similar purposes, but attributes provide a native, structured way to add metadata.
The Problem They Solve
Imagine you're building a web application. You need to:
- Define routes for different URLs
- Validate user input
- Control access permissions
- Cache certain results
Traditionally, you'd configure these in separate files or use comment blocks that PHP couldn't natively understand. Attributes let you attach this configuration directly to the relevant code, making it easier to read and maintain.
How Attributes Work
Here's a simple example :
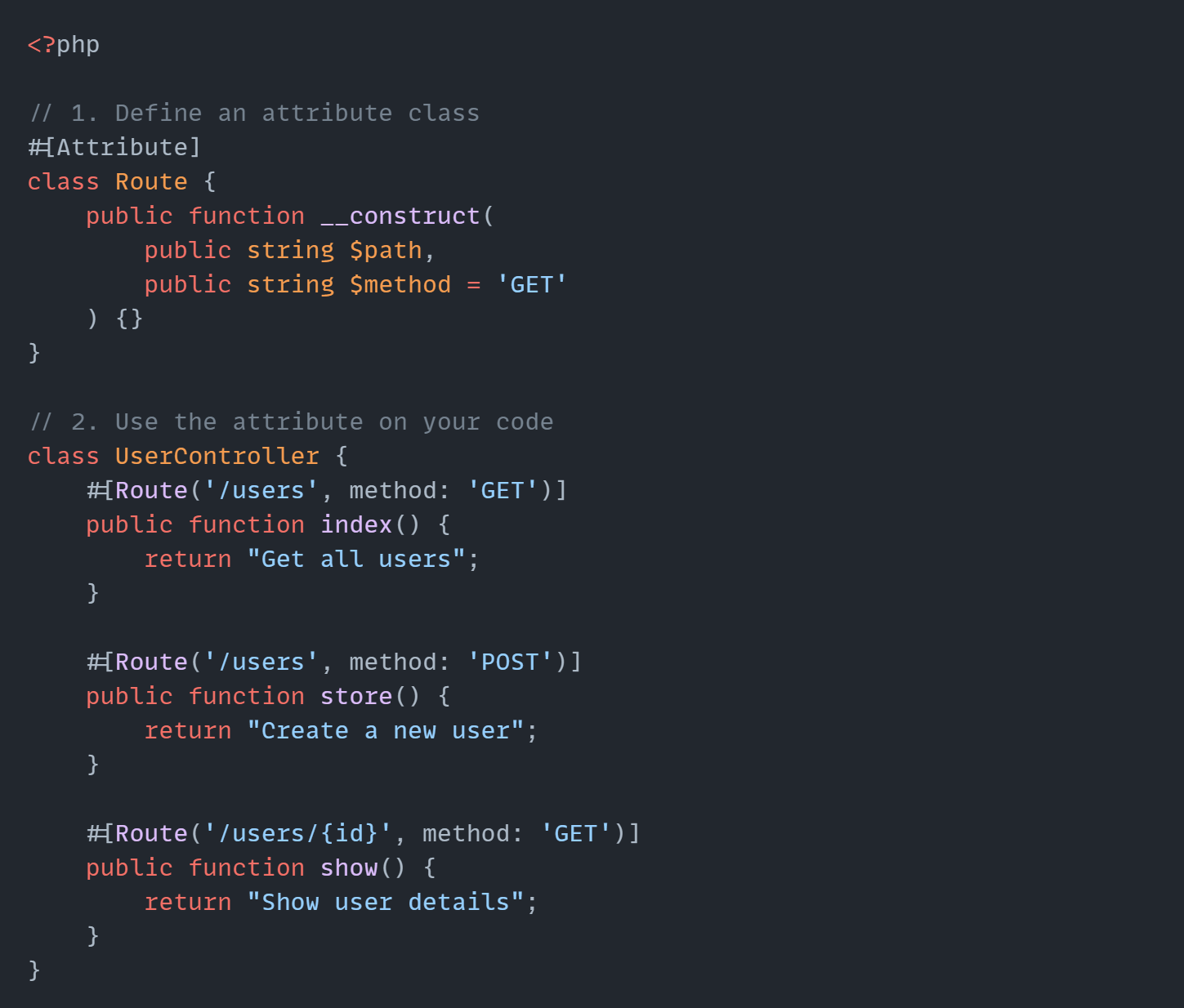
The #[Route] Syntax attaches routing information directly to each method. Clean and readable!
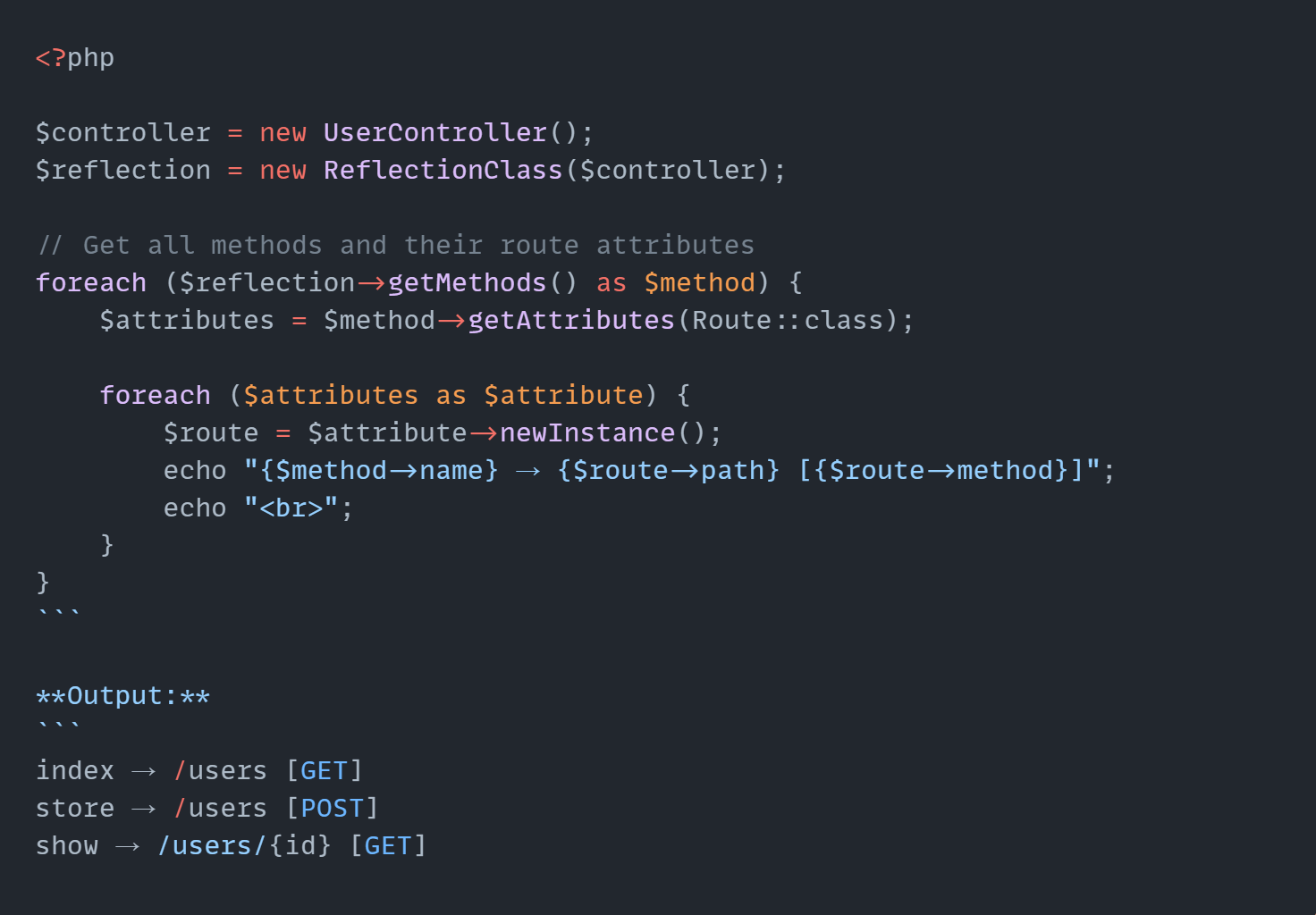
Reading Attributes at Runtime
PHP's Reflection API lets you read these attributes when your application runs:
Real-World Usage in Laravel
Laravel extensively uses attributes for cleaner, more intuitive code. Here are some examples:
1. Route Attributes (Laravel 10+)
Instead of defining routes in routes/web.php, you can use attributes:

2. Validation with Attributes
Laravel's validation can use attributes to define rules directly on request classes:

Why This Matters
Before attributes:
- Configuration scattered across multiple files
- Hard to see what's happening at a glance
- More code to maintain
With attributes:
- Configuration lives next to the code it affects
- Easier to understand and modify
- Type-safe and IDE-friendly
